Did you know that every year, over 7,000 different grape varieties are used to produce the wide range of wines enjoyed around the world? That’s right, the art of winemaking is a complex process that transforms humble grapes into the beloved beverage we all know and love.
If you’ve ever wondered how this magical transformation occurs, you’ve come to the right place. In this comprehensive guide, we will take you on a journey through the fascinating world of winemaking, from grape selection to the enjoyment of the finished product.
You’ll discover the importance of carefully choosing the right grapes and managing vineyards, as well as the crucial steps of harvesting and crushing the grapes to extract their precious juice.
We’ll delve into the science of fermentation, where the grape juice is transformed into wine, and explore how aging and maturation enhance the flavors and aromas.
Finally, we’ll reveal the final step of bottling the wine and the joy of savoring it.
So grab a glass, and let’s dive into the captivating process of how wine is made from grapes.
Table of Contents
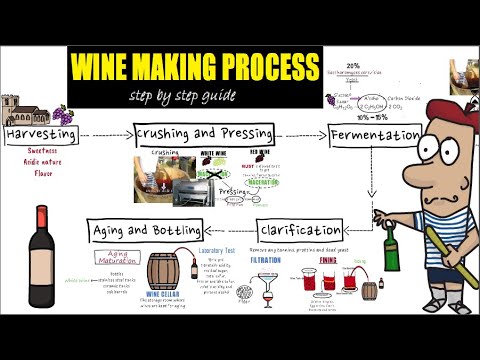
Related Video: "Wine making process step by step /Detail guide of wine making/preparation and making of wine" by Hospitality Broadcast
Key Takeaways
- Grape selection and vineyard management are crucial for desired taste and aroma in wine.
- Factors like climate, soil composition, and vineyard location determine the best grape variety for winemaking.
- The process of winemaking involves grape harvesting, crushing, pressing, and fermentation.
– Aging and maturation, including barrel aging, enhance the flavors and aromas of wine.
The Importance of Grape Selection and Vineyard Management
Choosing the right grapes and managing the vineyard with utmost care and dedication is crucial in crafting a wine that will tantalize your taste buds and leave you craving for more. Grape variety selection is the first step in this process. Different grape varieties have distinct flavor profiles, and winemakers carefully choose the ones that will create the desired taste and aroma.
Factors such as climate, soil composition, and vineyard location play a significant role in determining the grape variety that thrives best. Soil composition is another essential factor in grape selection and vineyard management. Different types of soil can contribute to the character of the wine. For example, sandy soil allows for better water drainage, resulting in grapes with concentrated flavors. On the other hand, clay soil retains more water, leading to wines with more structure and complexity.
Winemakers analyze the soil composition in their vineyards and make adjustments accordingly to ensure optimal grape growth and flavor development. Once the perfect grape variety is selected and the vineyard is managed with precision, the next step is harvesting and crushing the grapes. This crucial stage will be discussed in detail in the subsequent section, as it sets the foundation for the winemaking process.
Harvesting and Crushing the Grapes
Once the perfect moment arrives, it’s time to get hands-on and start harvesting and crushing those juicy clusters of goodness. This step is crucial in the winemaking process, as it sets the foundation for the flavor and quality of the final product.
Grape pressing is the first step after harvesting, where the grapes are gently pressed to extract the juice. This can be done manually or using mechanical presses. The goal is to separate the juice from the grape skins and seeds, which contain tannins and other compounds that contribute to the wine’s color, aroma, and flavor.
Next comes grape maceration, where the grape skins, pulp, and seeds are left in contact with the juice for a certain period of time. This allows the extraction of additional flavors, colors, and tannins from the grape solids. The duration of maceration depends on the desired style of wine, ranging from a few hours to several weeks.
After this step, the fermented grape juice is ready for the next phase: fermentation. This is where the magic happens, as the grape juice turns into wine through the action of yeast and the conversion of sugars into alcohol.
So, let’s dive into the fascinating world of fermentation and witness the transformation of grape juice into the beloved elixir we all know and love.
Fermentation: Turning Grape Juice into Wine
As the grape juice begins its transformative journey, the yeast acts as the alchemists of the winemaking process, converting sugars into alcohol and creating a bubbling concoction reminiscent of a lively symphony. This magical transformation is known as yeast fermentation, a crucial step in the creation of wine.
During fermentation, the yeast consumes the sugars in the grape juice, releasing carbon dioxide and alcohol as byproducts. This process not only adds the characteristic alcohol content to the wine but also contributes to its distinct flavors and aromas.
Temperature control plays a vital role in fermentation. The winemaker carefully monitors and adjusts the temperature to ensure the yeast functions optimally. Too high a temperature can lead to the yeast becoming stressed and producing off-flavors, while too low a temperature can slow down or even halt fermentation altogether. By maintaining the ideal temperature, the winemaker ensures that the yeast works its magic, creating a harmonious balance of flavors and preserving the natural essence of the grape.
Once fermentation is complete, the wine is ready for the next step: aging and maturation. During this phase, the wine will develop even more complex aromas and flavors, deepening its character and enhancing its overall quality. So, as the yeast finishes its transformative role, the wine eagerly awaits the next stage of its journey towards perfection.
Aging and Maturation: Enhancing Flavors and Aromas
Now that the yeast has worked its magic, it’s time for you to witness the transformation of your grape juice into a truly exquisite wine through the process of aging and maturation.
This stage is where the true artistry of winemaking takes place, as flavors and aromas deepen and develop over time. Barrel aging is a crucial step in this process, as it imparts unique characteristics to the wine. Oak barrels are commonly used, as they add flavors such as vanilla, spice, and toastiness, enhancing the complexity of the final product. The wine rests in these barrels for months or even years, allowing it to absorb these delightful nuances.
Another method of aging is oxidative aging. This involves exposing the wine to oxygen, which can influence its taste and texture. The wine is transferred to a different vessel, often made of glass or stainless steel, where it is exposed to controlled levels of oxygen. This process can contribute to the development of nutty, caramel flavors that add depth and richness to the wine.
As the wine ages and matures, its flavors become more refined and harmonious. Once the desired level of aging has been achieved, it is time to move on to the next step: bottling and enjoying the finished product.
The careful process of aging and maturation has transformed your grape juice into a wine that’s ready to be savored and appreciated.
Bottling and Enjoying the Finished Product
Indulge in the exquisite pleasure of savoring and relishing the finished product, as the culmination of your winemaking journey is finally bottled and ready to be enjoyed.
After the aging and maturation process, it’s time to carefully transfer the wine into bottles for storage. This step is crucial in preserving the flavors and aromas you’ve worked so hard to develop.
Wine storage plays a vital role in maintaining the quality of your wine. It’s important to store your bottles in a cool, dark place with a consistent temperature to avoid spoilage. The ideal temperature is around 55°F (13°C), as excessive heat can speed up the aging process and negatively impact the wine’s taste.
When it comes to enjoying your wine, pairing it with the right food can enhance the overall experience. The flavors and textures of the food can complement or contrast with the wine, creating a harmonious balance. Red wines, such as Cabernet Sauvignon or Merlot, pair well with red meats and hearty dishes, while white wines like Chardonnay or Sauvignon Blanc are often paired with seafood, poultry, or light pasta dishes.
So, take pleasure in the art of wine appreciation. Let the beauty of the bottle and the anticipation of the first sip fill you with excitement. Cheers to the fruits of your labor!
Frequently Asked Questions
How long does it take for grapes to ferment into wine?
Grape fermentation time varies depending on factors like grape variety and desired wine style. Generally, it takes about 1-2 weeks for primary fermentation, followed by a secondary fermentation that can last several months to years.
What is the ideal temperature for fermenting grape juice into wine?
The ideal temperature for fermenting grape juice into wine is around 68-72 degrees Fahrenheit. Fermenting at this temperature allows for a slow and controlled process, resulting in a balanced and flavorful wine. Different temperatures can affect the aromas and flavors of the wine, so it’s important to choose the right temperature for the desired outcome.
Can different types of grapes be mixed together to make wine?
Did you know that wine blending is a common practice, with winemakers often mixing different grape varieties to create unique flavor profiles? It’s a fascinating way to experiment and craft a truly exceptional wine.
How is the alcohol content of wine determined?
The alcohol content of wine is determined through alcohol content measurement methods, such as using a hydrometer or refractometer. Factors affecting alcohol content include grape variety, sugar levels, fermentation process, and winemaker’s decisions.
Are there any health benefits associated with drinking wine?
Drinking wine in moderation can have health benefits! Studies show that wine, with its antioxidants, can improve cardiovascular health and reduce the risk of heart disease. Cheers to good health!



